This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the current version.
This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the current version.Offline Backup
Offline backup (or backup via saved state) is another native Hyper-V approach to quiescing VMs before taking a volume snapshot. This type of backup requires some downtime of a VM. When a VM is backed up, the Hyper-V VSS Writer forces the VM into the saved state to create a stable system image.
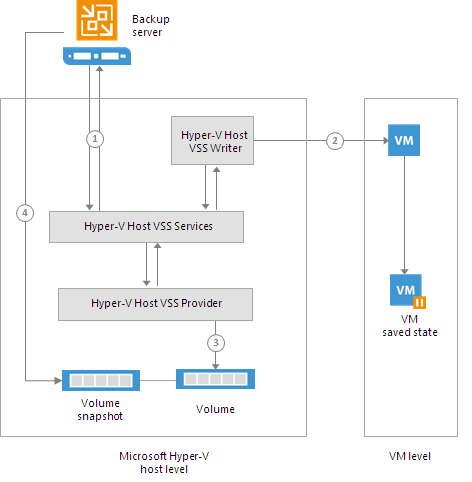
Offline backup is performed in the following way:
- Veeam Backup & Replication interacts with the Hyper-V host VSS Services and requests backup of specific VMs.
- The Hyper-V host VSS Writer forces a VM into the saved state for several seconds. The VM OS hibernates and the content of the system memory and CPU is written to a dump file.
- The Hyper-V host VSS provider takes a snapshot of a volume on which the VM is located. After the snapshot is created, the VM returns to the normal state.
- The volume snapshot is presented to Veeam Backup & Replication. Veeam Backup & Replication reads VM files from the volume snapshot using one of two backup modes — on-host backup or off-host backup. After the backup is completed, the snapshot is deleted.
Offline backup may be inappropriate — it incurs downtime to a VM and does not produce transactionally consistent backups and replicas as Veeam Backup & Replication does not interact with the VSS framework on the VM guest OS during backup or replication. As an alternative to offline backup, Veeam Backup & Replication offers the crash-consistent backup method for those cases when online backup is not possible and offline backup is unsuitable.