 This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the current version.
This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the current version.Backup Chain Detection
Veeam Backup & Replication will transfer to the capacity extent only those restore points that belong to inactive backup chains. To ensure a backup chain is inactive, Veeam Backup & Replication verifies its state. This does not apply to the copy policy: all newly created restore points are copied immediately.
Inactive Backup Chain of a Backup Job
When a backup job runs for the first time, Veeam Backup & Replication creates an initial full backup file. It contains complete information about the VMs that are being backed up. With each subsequent backup job session, new incremental backup files are created. They contain only the changes that have occurred since the last backup session.
For forward incremental backup method, the active backup chain is the one that has not yet been sealed with a new full backup file.
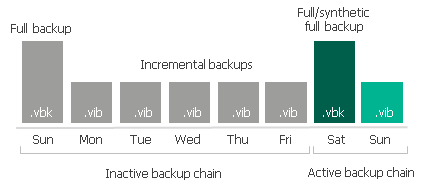
To transform an active backup chain into inactive, a new active full (or synthetic full) backup file must be created for this chain. This can be done either manually, as described in Performing Active Full Backup. Else, you can configure a schedule according to which new active or synthetic full backups will be created automatically, as described in Active Full Backup and Synthetic Full Backup.
Once a new full backup file is created and the offload session is being executed, Veeam Backup & Replication collects all the restore points (full and incremental) that were created prior to the latest active full, verifies that they belong to an inactive chain, and prepares them to be moved to the capacity extent. This process is called detect. For more information, see Moving Backups to Capacity Tier.
Note that Veeam Backup & Replication will not transfer to the capacity tier the corrupted restore points and the files dependent on those. For more information on the corrupted restore points, see Health Check for Backup Files.
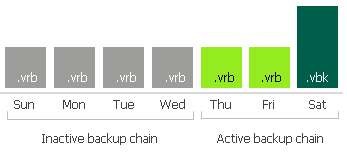
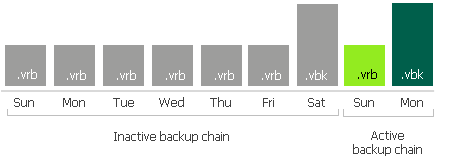
The same applies to the backup chains created with the reverse-incremental method. In this case, all the .vrb files starting from the third restore point will be considered inactive automatically. Thus, you do not need to create an active full (nor synthetic full) backup manually unless you want to offload all the restore points including the most recent .vbk file and the first two .vrb files.
Consider the following examples:
- Four .vrb files are inactive and can be offloaded:
- Six .vrb files and a .vbk file belong to an inactive chain and can be offloaded:
|
Mind that a full backup file and the first two incremental backup files (that is, two .vrb files that immediately follow the most recent .vbk file) will not be offloaded until another full backup file is created successfully. |
The structure of the backup chains can be different. That depends on whether your backups were created using the per-VM method (for more information, see Per-VM Backup Files) or as a single storage, with all VMs placed into a single file. The type of the backup chain structure does not affect the offload process.
For more information on how Veeam Backup & Replication creates and manages backup chains, see Backup Chain.
Inactive Backup Chain of a Backup Copy Job
When offloading backup chains created by backup copy jobs, Veeam Backup & Replication will move only full backup files that have a GFS flag.
To enable the GFS retention policy for the files, select the following check boxes at the Target step of the New Backup Copy Job wizard:
- Keep the following restore points as full backups for archival purposes check box
- [Optional] Read the entire restore point from source backup instead of synthesizing it from increments.
For more information on how to configure a backup copy job and how the GFS retention works, see Creating Backup Copy Jobs and GFS Retention Policy respectively.
Consider the following examples:
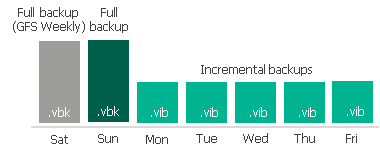
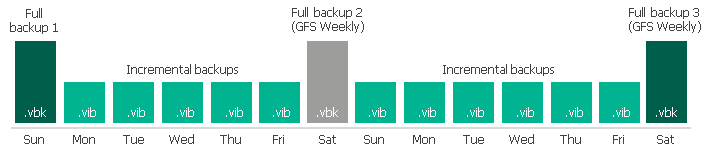
- A backup chain consists of two .vbk files and five .vib files created with the synthetic full method.
The weekly full backup file has a GFS flag (Weekly) assigned to it and can be offloaded to object storage. The second full backup file cannot be offloaded until it is also assigned a GFS flag. It will happen after another full backup file is created.
- A backup chain consists of three .vbk files and 11 .vib files created with the active full method.
In this case, the full backup file 1 does not have any GFS flag and will not be offloaded at all.
A full backup file 2 has a Weekly flag, so it can be offloaded to object storage. The full backup file 3 also has a Weekly flag, but this file is active. It will not be offloaded until another full backup file is created.
|
The following types of backup files are never offloaded from backup chains created by backup copy jobs:
|