This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the current version.
This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the current version.How Repository with Rotated Drives Works
You can use Microsoft Windows server or Linux server or SMB (CIFS) share as a backup repository with rotated drives.
Microsoft Windows Backup Repository
Veeam Backup & Replication performs backup jobs and backup copy jobs targeted at a backup repository with rotated drives in different ways.
Important |
When you specify retention settings for a backup job or a backup copy job targeted at a backup repository with rotated drives, you must define the total number of restore points that you want to retain on all drives in the set. You can specify retention in days or restore points. For example, if you set retention to 14 restore points, the job will keep the total of 14 restore points across all drives. Before the drive change, we recommend to check the retention setting in backup chains on all drives in the set. Otherwise, Veeam Backup & Replication will delete all restore points on the drive that you plan to use in the following cases:
To eliminate the risk of deleting a backup chain from a rotated drive, make sure you have increased the retention value. You can also disable a backup copy job before you will use the drive. |
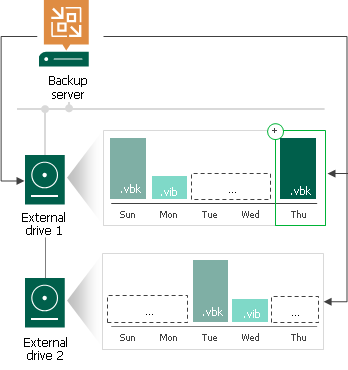
Backup Jobs
Backup jobs are performed in the following way:
- Veeam Backup & Replication creates a regular backup chain on the currently attached drive.
- When a new job session starts, Veeam Backup & Replication checks if the backup chain on the currently attached drive is consistent. The consistent backup chain must contain a full backup and all incremental backups that have been produced by the job. This requirement applies to all types of backup chains: forever forward incremental, forward incremental and reverse incremental.
If external drives have been swapped, and the full backup or any incremental backups are missing from the currently attached drive, Veeam Backup & Replication starts the backup chain anew. It creates a new full backup file on the drive, and this full backup is used as a starting point for subsequent incremental backups.
- [For external drives attached to Microsoft Windows servers] Veeam Backup & Replication checks the retention policy set for the job. If some backup files in the backup chain are outdated, Veeam Backup & Replication removes them from the backup chain.
- When you swap drives again, Veeam Backup & Replication checks the backup chain for consistency and creates a new full backup.
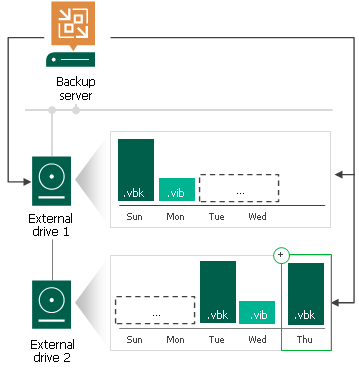
Backup Copy Jobs
Backup copy jobs are performed in the following way:
- Veeam Backup & Replication creates a regular backup chain on the currently attached drive.
- When you swap drives, and the attached drive is empty, Veeam Backup & Replication creates a full backup on it. If there is a backup chain on the drive, Veeam Backup & Replication creates a new incremental backup and adds it to the backup chain. The latest incremental backup existing in the backup chain is used as a starting point for the new incremental backup.
- [For external drives attached to Microsoft Windows servers] Veeam Backup & Replication checks the retention policy set for the job. If some backup files in the backup chain are outdated, Veeam Backup & Replication removes them from the backup chain.
Drive letters for external drives may change when you add new volumes or storage hardware such as CD-ROM on the server. In Microsoft Windows backup repositories, Veeam Backup & Replication can keep track of drives and detect them even if the drive letter changes.
To detect a drive correctly, Veeam Backup & Replication must have a record about it in the configuration database. Consider the following requirements:
- When you insert a drive for the first time, the drive is not registered in the configuration database. Such drive must have the same letter as the one specified in the Path to folder field in backup repository settings. For more information, see Configuring Path and Load Control Settings.
If the drive has some other letter, Veeam Backup & Replication will not be able to detect and use it.
- When you insert a drive that has already been used and has some restore points on it, the drive is already registered in the configuration database. Veeam Backup & Replication will be able to detect and use it, even if the drive letter changes.
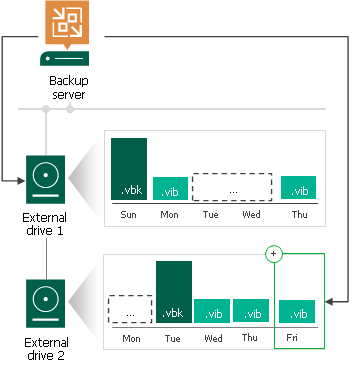
Linux and Shared Folder Backup Repository
If you use a Linux server or CIFS share as a backup repository with rotated drives, Veeam Backup & Replication employs a “cropped” mechanism of retention with rotated drives. Veeam Backup & Replication keeps information only about the latest backup chain in the configuration database. Information about previous backup chains is removed from the database. For this reason, the retention policy set for the job may not work as expected.
A job targeted at a backup repository with rotated drives is performed in the following way:
- During the first run of the job, Veeam Backup & Replication creates a regular backup full backup on the drive that is attached to the backup repository server.
- During the next job session, Veeam Backup & Replication checks if the current backup chain on the attached drive is consistent. The consistent backup chain must contain a full backup and all incremental backups subsequent to it. This requirement applies to all types of backup chains: forever forward incremental, forward incremental and reverse incremental.
- If the current backup chain is consistent, Veeam Backup & Replication adds a new restore point to the backup chain.
- If external drives have been swapped, and the current backup chain is not consistent, Veeam Backup & Replication always starts a new backup chain (even if restore points from previous backup chains are available on the attached drive). Veeam Backup & Replication creates a new full backup file on the drive, and this full backup is used as a starting point for subsequent incremental backups.
As soon as Veeam Backup & Replication starts a new backup chain on the drive, it removes information about restore points from previous backup chains from the configuration database. Backup files corresponding to these previous restore points are not deleted, they remain on disk. This happens because Veeam Backup & Replication applies the retention policy only to the current backup chain, not to previous backup chains.