 This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the current version.
This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the current version.Backup Chain
If you enable image-level backups for a backup policy, Veeam Backup for Google Cloud creates a new backup in a standard or nearline repository during every backup session. A sequence of backups created during a set of backup sessions makes up a regular backup chain.
The regular backup chain includes backups of the following types:
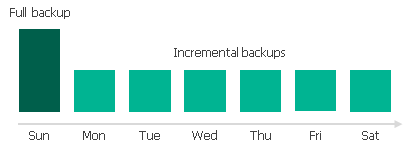
- Full — a full backup stores a copy of the full instance image.
- [Applies only to VM instances] Incremental — incremental backups store incremental changes of the instance image.
VM Backup Chain
To create a regular backup chain for a VM instance protected by a backup policy, Veeam Backup for Google Cloud implements the forever forward incremental backup method:
- During the first backup session, Veeam Backup for Google Cloud copies the full instance image and creates a full backup in the standard or nearline repository. The full backup becomes a starting point in the regular backup chain.
- During subsequent backup sessions, Veeam Backup for Google Cloud copies only those data blocks that have changed since the previous backup session, and stores these data blocks to incremental backups in the standard or nearline repository. The content of each incremental backup depends on the content of the full backup and the preceding incremental backups in the regular backup chain.
Veeam Backup for Google Cloud creates incremental backups based on the Veeam proprietary filtering mechanism that filters out unchanged data blocks by calculating a checksum for every block. The Google Cloud changed block tracking (CBT) mechanism that would allow tracking changed blocks of data and would increase the efficiency of incremental backups is not implemented at the moment.
Full and incremental backups act as restore points for backed-up instances that let you roll back instance data to the necessary state. To recover an instance to a specific point in time, the chain of backups created for the instance must contain a full backup and a set of incremental backups dependent on the full backup.
If some backup in the regular backup chain is missing, you will not be able to roll back to the necessary state. For this reason, you must not delete individual backups from the backup repository manually. Instead, you must specify retention policy settings that will let you maintain the necessary number of backups in the repository. For more information, see Retention Policy for Backups.
Cloud SQL Backup Chain
The forever forward incremental backup method is not implemented for Cloud SQL instances — during every backup session Veeam Backup for Google Cloud creates a full backup in the regular backup chain.
Each Cloud SQL backup in the backup chain contains metadata that stores information about the protected Cloud SQL instance, the backup policy that created the backup, as well as the date, time and configured retention settings. Veeam Backup for Google Cloud uses metadata to identify outdated backups, to retrieve information on the source instance configuration during recovery operations, and so on.
Cloud SQL backups act as independent restore points for backed-up Cloud SQL instances. If you remove any backup, it will not break the backup chain — you will still be able to roll back data to any existing restore point.
The period of time during which Cloud SQL backups are kept in the backup chain is defined by retention policy settings. For details, see Retention Policy for Backups.
Related Topics