This document is not maintained any longer.
This document is not maintained any longer.Set Up VPN Between Microsoft Azure and Local Sites
You can use Veeam PN to set up a VPN connection between private clouds in Microsoft Azure and local company sites. This scenario can be helpful if you have moved some of your application and services to Microsoft Azure. In this case, you can join Microsoft Azure networks with local company networks over the VPN and enable secure communication between remote sites.
Reference Environment
This how-to assumes that your company environment is distributed between two sites:
- Microsoft Azure: part of your applications and services are hosted in Microsoft Azure.
- Local company site: part of your applications and services are hosted on a local company site.
In this scenario, you will deploy Veeam PN components in the following way:
- Network hub will be hosted in Microsoft Azure.
- Site gateway will be hosted on the local company site.
The network hub and site gateway will produce the two terminal points of a VPN tunnel. Application and services in Microsoft Azure and on the local company site will be able to securely communicate over the VPN tunnel. Users on the local company site will be able to get access to company resources in Microsoft Azure.

Prerequisites
To follow instructions of this how-to, check the following prerequisites:
- You must have a user account in Microsoft Azure.
- You must use the Azure Resource Manager model to configure the network hub in Microsoft Azure. The classic deployment model is not supported.
- You must have a VMware vSphere host on the local company site. A site gateway is deployed as a virtual appliance and placed on the VMware vSphere host.
Step-By-Step Walkthrough
To set up a VPN connection between a private cloud in Microsoft Azure and a local company site, you will:
- Deploy the network hub in Microsoft Azure.
- Register a client for the local site network in the Veeam PN portal.
- Deploy a site gateway in the local site network.
- Add Static Routes for Outgoing Traffic on Default Gateways
Step 1. Deploy Network Hub in Microsoft Azure
The network hub is the core of the VPN infrastructure. If you want to join a Microsoft Azure network with a local site network, you must deploy the network hub in Microsoft Azure.
To deploy the network hub:
- Sign in to the Microsoft Azure portal at https://portal.azure.com.
- In the menu on the left, click New.
- In the marketplace, search for the 'Veeam PN for Microsoft Azure' template.
- Select the template and click Create.
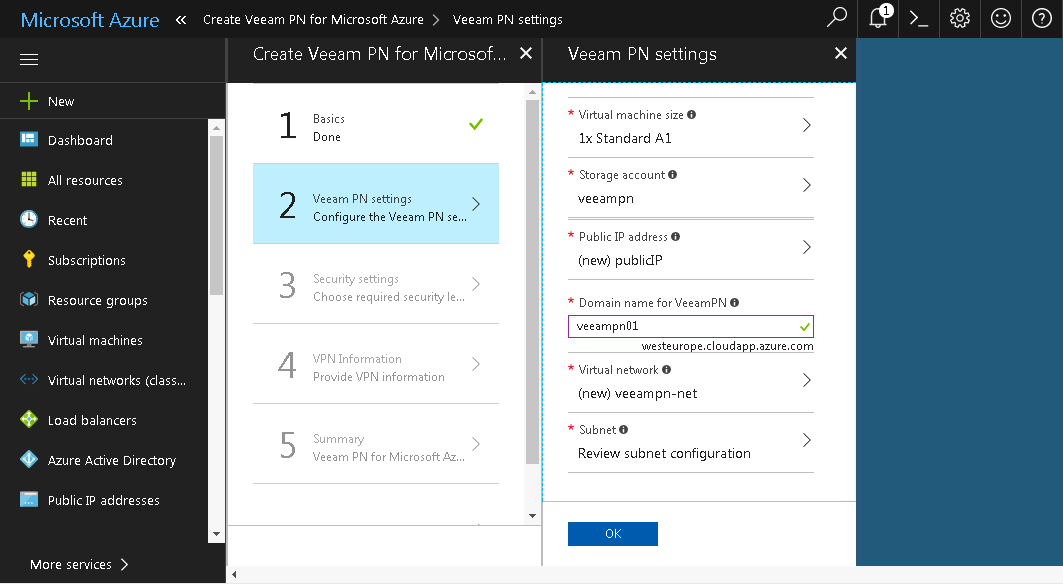
- On the Basics blade, specify basic VM settings: VM name, user credentials for the network hub administrator account, subscription, resource group and location.
- On the Veeam PN settings blade, specify basic settings for the network hub appliance: VM size (A1 size is minimum), storage account, public IP address, domain name, virtual network and subnet.
- On the Security settings blade, specify parameters for the self-signed SSL certificate that Veeam PN will use to secure connection in the VPN: the certificate key length.
- On the VPN Information blade, make sure that Yes is enabled in the Enable Site-to-Site field. In the Specify a protocol and Specify a port fields, leave default settings.
- On the Summary blade, click OK.
- On the Buy blade, click Purchase.
Veeam PN will deploy the network hub from the Microsoft Azure template. The deployment process typically takes several minutes. Wait for this process to complete.
- In the Microsoft Azure portal, open properties of the deployed appliance and get its IP address.
- In a web browser, access the Veeam PN portal by the following address: https://<networkhubIP>.
The browser will display a warning notifying that the connection is untrusted. Ignore the warning and agree to proceed to the portal.
- At the Welcome screen, log in to the portal under the network hub administrator account. You specified credentials for the network hub administrator account on the Basic blade.
- Click Login.
- On the welcome screen of the Azure Setup wizard, click Next.
- The Azure Setup wizard will display the https://aka.ms/devicelogin link and an authentication code. Copy the code to the Clipboard, open the https://aka.ms/devicelogin link in a web browser and enter the code in the code field.
- Click Next. Veeam PN will assign the Network Contributor role on the routing table in the Microsoft Azure network to the network hub administrator account. Wait for the process to complete and click Finish.
Step 2. Register Client for Local Site Network in Veeam PN Portal
To add a local site network to the VPN, you must register a client for this local network in the Veeam PN portal. Veeam PN will generate a configuration file for the local site network. You will use the configuration file to set up a site gateway in the local site network.
To register a client for the local site network:
- In the Veeam PN portal, in the configuration menu on the left click Clients.
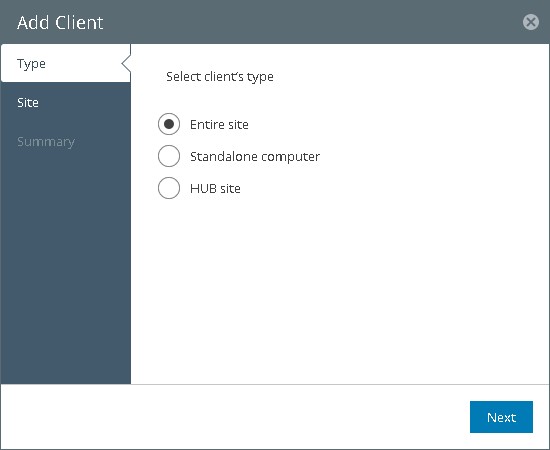
- At the top of the clients list, click Add.
- At the Type step of the wizard, select Entire site.
- At the Site step of the wizard, enter a name and address of the local site network using the CIDR notation.
- At the Summary step of the wizard, click Finish.
Veeam PN will generate an XML file with VPN settings for the local site network. The XML file will be automatically downloaded to the default downloads folder. Save the downloaded file in a network shared folder accessible from the local site network.
Step 3. Deploy Site Gateway in Local Site Network
When you deploy the network hub in Microsoft Azure, you configure one point of the VPN tunnel. To configure the other point of the VPN tunnel, you must deploy a site gateway on the local company site. The site gateway establishes a VPN connection with the network hub in Microsoft Azure, which lets data to travel securely over a public connection between remote sites.
To deploy a site gateway in the local site network:
- Download the Veeam PN OVA package from: https://www.veeam.com/downloads.html and save it in a network shared folder accessible from the local site network.
- In VMware vSphere Web Client, open the hosts and clusters inventory list and select a host on which you want to place the site gateway.
- From the menu at the top of the working area, select Actions > Deploy OVF Template.
- At the Select source step of the wizard, select Local file, click Browse and browse to the Veeam PN OVA package.
- Follow the next steps of the wizard and specify site gateway settings: datastore on which the site gateway VM disk must be placed, disk format, network to which the site gateway must be connected and so on.
- At the last step of the wizard, select the Power on after deployment check box and click Finish.
Veeam PN will deploy the site gateway on the selected host. The deployment process typically takes several minutes. Wait for the process to complete and proceed to site gateway configuration.
- In VMware vSphere Web Client, navigate to the Summary tab and get an IP address of the deployed site gateway.
- In a web browser, access the site gateway portal by the following address: https://<sitegatewayIPaddress>.
The browser will display a warning notifying that the connection is untrusted. Ignore the warning and agree to proceed to the portal.
- At the Welcome to Veeam PN screen of the portal, enter the credentials for the built-in administrator acount:
- Username: root
- Password: VeeamPN
- Click Login. When prompted, change the password for the built-in administrator account.
- At the first step of the Initial Configuration wizard, select Site gateway.
- Click Browse and browse to the configuration file for the local site network generated by Veeam PN.
- Click Finish.
Step 4. Add Static Routes for Outgoing Traffic on Default Gateways
By default, when a machine in one remote site needs to communicate with a machine in another remote site, it sends a request over the default site gateway. To route traffic going between sites over the VPN tunnel, you need to add static routes on default gateways on both sites. These static routes will destine the traffic from the default gateway to the Veeam PN appliance — network hub or site gateway, which, in its turn, will route traffic through the VPN tunnel between the two sites.
For example, Site A and Site B have the following configuration:
Site A: 192.168.0.0/24
- Network mask: 255.255.255.0
- Site gateway IP address: 192.168.0.2
- Default gateway IP address: 192.168.0.1
- Client machine IP address: 192.168.0.14
Site B: 172.17.53.0/24
- Network mask: 255.255.255.0
- Site gateway IP address: 172.17.53.2
- Default gateway IP address: 172.17.53.1
- Client machine IP address: 172.17.53.12
If a machine in Site A needs to communicate with a machine in Site B, the traffic will first be sent to the default gateway 192.168.0.1. The default gateway must then route the traffic to the site gateway that, in its turn, will route the traffic through the VPN tunnel. For this reason, you must add the following route on the default gateway 192.168.0.1:
route add 172.17.53.0 mask 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.2 |
In a similar manner, you must add a route on the default gateway 172.17.53.1 in Site B:
route add 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0 172.17.53.2 |
Result
You have set up a VPN connection between a Microsoft Azure network and local site network. VMs running in Microsoft Azure are now accessible from the local site network, and vice versa.