 This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the current version.
This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the current version.Mount Server
The mount server is required if you perform restore VM guest OS files and application items to the original location. The mount server lets you route VM traffic by an optimal way, reduce load on the network and speed up the restore process.
When you perform file-level restore or application item restore, Veeam Backup & Replication needs to mount the content of the backup file to a staging server. The staging server must be located in the same site as the backup repository where backup files are stored. If the staging server is located in some other site, Veeam Backup & Replication may route data traffic in a non-optimal way.
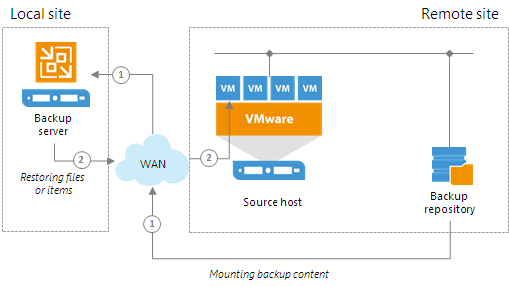
For example, if the backup server is located in the local site while the source host and backup repository are located in the remote site, during restore to original location Veeam Backup & Replication will route data traffic in the following way:
- From the remote site to the local site — to mount the content of the backup file to the staging server.
- From the local site to the remote site — to restore files or application items.
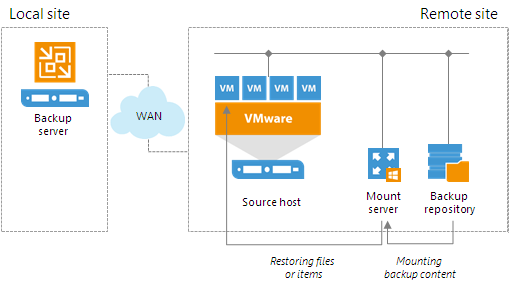
To prevent VM data from traveling between sites, Veeam Backup & Replication uses the mount server. The mount server acts as a "mount point" for backups in the backup repository. When you restore files or application items to the original location, Veeam Backup & Replication mounts the content of the backup file to the mount server (or the original VM for restore to the Microsoft SQL Server and Oracle VMs) and copies files or items to their destination via this mount server or VM. For more information about possible mount points, see File-Level Restore Scenarios.
The mount server is created for every backup repository and associated with it. When you configure a backup repository, you define which server you want to use as a mount server for this backup repository. By default, Veeam Backup & Replication assigns the mount server role to the following machines:
- Backup repository. For Microsoft Windows backup repositories, the mount server role is assigned to the backup repository server itself.
- Backup server. For Linux, shared folder backup repositories and deduplicating storage appliances, the mount server role is assigned to the backup server.
- Veeam Backup & Replication console. The mount server role is also assigned to a machine on which the Veeam Backup & Replication console is installed. Note that this type of mount server is not registered in the Veeam Backup & Replication configuration database.
For scale-out backup repositories, you must define the mount server for every extent.
If you do not want to use default mount servers, you can assign the mount server role to any Microsoft Windows machine in the backup infrastructure. It is recommended that you configure at least one mount server in each site and associate this mount server with the backup repository residing in this site. The mount server and backup repository must be located as close to each other as possible. In this case, you will be able to keep the VM traffic in one site.
Services and Components
On the mount server machine, Veeam Backup & Replication installs the Veeam Mount Service. The Veeam Mount Service requires .NET 4.5.2. If .NET 4.5.2 is not installed on the machine, Veeam Backup & Replication will install it automatically.
Requirements to Mount Server
The machine to which you assign the mount server role must meet the following requirements:
- You can assign the role of a mount server to Microsoft Windows machines (physical or virtual).
- You can assign the role of a mount server to 64-bit machines only.
- The mount server must have access to the backup repository with which it is associated and to the original VM (VM to which you restore files or application items). For restore from storage snapshots, the mount server must also have access to the ESX(i) host on which the temporary VM is registered.
Related Topics