This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the current version.
This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the current version.Using Oracle Restore Wizard
In this article
- Specify connection settings for target server where the database should be restored:
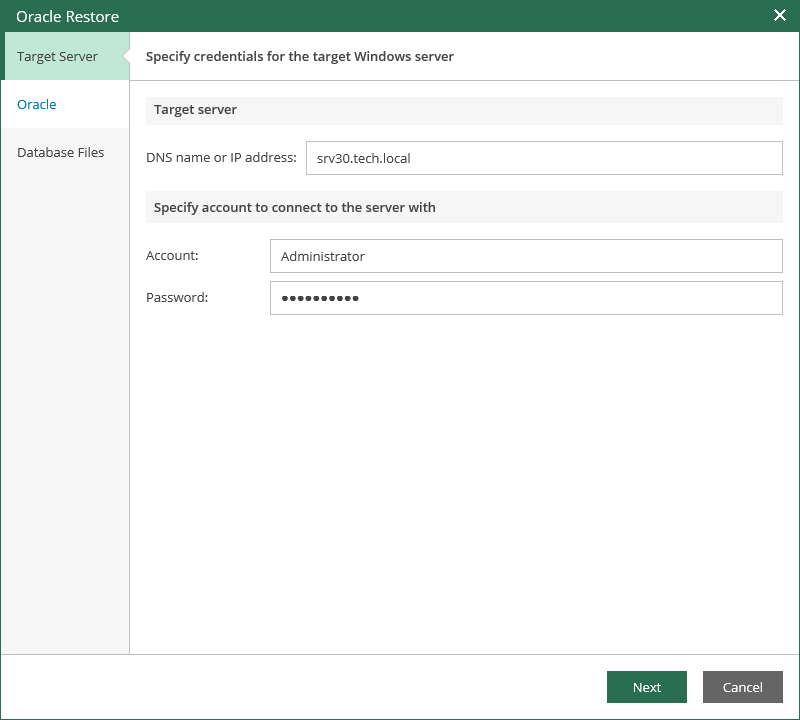
- If you are restoring Oracle on Windows:
- Enter DNS name or IP address of the target Windows machine.
- Specify the account to be used for connection with the target Windows-based Oracle server. Make sure the account has the sysdba rights on that server (Windows authentication will be used). To be able to copy archived logs from backup to the target server for further replay (in case of restore to certain point in time), the account should be also granted sufficient permissions to access the administrative share on that machine (for example, \\myserver\C$): Read and Write are minimal required, Full Control recommended.
- If you are restoring Oracle on Linux, specify connection settings for the target Linux server:
- Server name (or IP address) and SSH port – default port is 22.
- Account to be used to access the server. This should be a root account or account elevated to root and added to sudoers. To elevate the account and add it to sudoers, click Settings and use the corresponding options.
You can use authentication by user name and password or by private key.
- Next, select Oracle Home and specify Global database name and Oracle SID where to restore the database from backup.
- Consider that if database with the specified Oracle SID exists on the target Oracle home, the restore process by design will delete it and replace with the database from backup. Thus, before starting the restore process, a message will be displayed, asking you to confirm the operation.