Scenario 1: Restore to Current Restore Point
This scenario allows you to restore a database to the state as of at the moment when selected restore point was created. Consider the following:
- You will not need to perform Oracle redo logs replay, so ARCHIVELOG can be turned on or off for the Oracle database. If it is turned on, you can select any log handling option on the Oracle tab of the VM guest processing settings in the backup job.
- Use the Oracle Database Restore Wizard to specify the necessary VM restore point and automatically add it to Veeam Explorer scope.
- During database restore process, selected restore point will be mounted to the specified Oracle server (this can be original or different server) and recovered with RMAN and Veeam Backup & Replication restore capabilities, as described in this guide.
Scenario 2: Restore to Selected Point in Time
This scenario allows you to restore a database to the state as of at the selected point in time. Consider the following:
- Veeam Explorer will need to perform Oracle redo logs replay, so ARCHIVELOG must be turned ON for the Oracle database.
- You can select any log handling option on the Oracle tab of the VM guest processing settings of the backup job. However, if you select any of Truncate logs options, remember that this will turn on log truncation on VM guest file system (that is, within image-level backup). So, in this case you can either:
- Select to Backup logs to Veeam repository,
or
- Make sure that truncation conditions are configured so that logs required for replay will be available when necessary.
- Use the Oracle Database Restore Wizard to specify the necessary VM restore point and automatically add it to Veeam Explorer scope, as described in the “Automated Recovery” section below.
- Database will be recovered to the closest VM restore point before the moment you specify, and then log replay will be performed on the target Oracle server to bring the database to the necessary state.
|
Current version does not support this scenario for replicas or backups archived to the secondary location using backup copy jobs. |
Scenario 3: Restore to Selected Transaction
To restore a database to the state as of prior to selected transaction, you will also need a staging Oracle server. The process will go as follows:
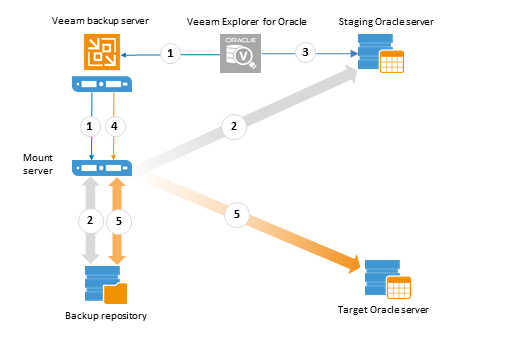
1, 2 To present the list of transactions to user, Oracle database is mounted to staging server, and redo log backups are also copied there, so consider the recommendations listed in points 1 and 2 for Scenario 2.
3 A user selects the undesired transaction, instructing Veeam to restore database to the state prior to that operation.
4, 5 After a user invokes the Restore command, database backup is mounted to the target Oracle server, and log files are copied there. Log replay is performed with the closest earlier restore point on target Oracle server to bring the database to desired state. After the database is ‘re-created’ the Oracle server, it becomes ready for use.
|
You can use the same Oracle server as a staging system and as a target server. |
Related Topic
Scenario 1: Restoring a Database to Current Restore Point
Scenario 2: Restoring a Database to Specific Point in Time
Scenario 3: Restoring a Database to Specific Transaction







