Paragraphs
To help users browse through content more effectively and make your topics clearer, follow the next guidelines when writing paragraphs.
Tip |
Before you start working with a topic, answer the following questions:
|
One Idea per Paragraph
Build each paragraph around one key point and describe the point within the first 2 sentences. The rest of the paragraph must deal with describing and extending that key point.
Users often run through topics by reading the first sentence of each paragraph. So, if you cover only one idea per paragraph, you help readers quickly get to the point and choose whether to read the rest of the paragraph or not.
Explicit Paragraph Structure
The first 2 paragraphs in each topic must state the most important information. The introductory paragraph (that is, the topic sentence) must be followed by paragraphs that contain essential details explaining your overall topic. After that, add general information and whatever secondary details you consider helpful.
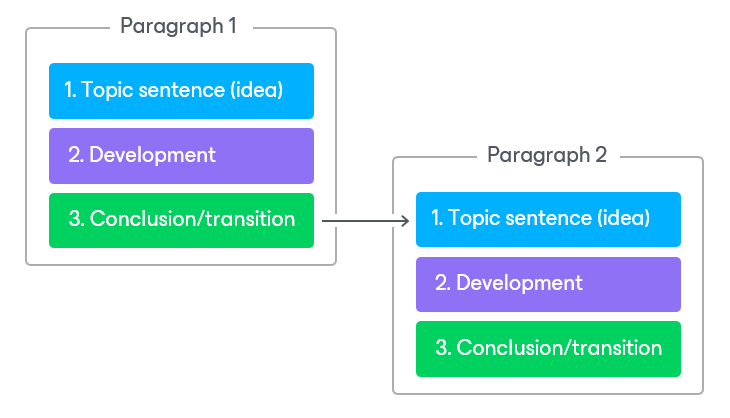
Build each paragraph based on the following structure:
- Introduce an idea in a topic sentence and make it as clear as possible. Do not overload the idea with unnecessary details.
For more information on topic sentences, see the YourDictionary online reference, section Examples of Topic Sentences.
- Develop the idea, explain it, provide details, examples and so on.
- Add conclusion or transition to a new idea in the next paragraph.
For more information on how to build paragraphs, see the Purdue Online Writing Lab resources, section On Paragraphs.
Limited Paragraph Length
Keep the number of sentences in each paragraph between 3 and 5. Paragraphs should be no longer than 40–70 words and no more than 5 lines.
Limited Number of Paragraphs
If there are more than 5 or 6 sequential paragraphs in a topic, consider restructuring the topic and creating several subtopics.
Tip |
After you finish working with a topic, answer the following questions:
|
Example
To guarantee the recoverability of your data, Veeam Backup & Replication complements the SureBackup recovery verification technology with SureReplica. [key point; transition] SureReplica is in many respects similar to SureBackup recovery verification. It lets you validate your DR environment without impacting the production infrastructure. You can automatically verify every created restore point of every VM replica and ensure that they are functioning as expected. [essential details; transition] The SureReplica technology is not limited only to VM replica verification. Just like SureBackup, it provides the following capabilities: [additional info]
|