Restore scenarios are implemented as follows:
- Target SQL Server is used to perform the restore operations. Depending on the scenario, the corresponding backup data is utilized (the restore points closest to the specified time or transaction, and transaction log backups). In the Restore to selected point in time and Restore to the state before selected transaction scenario, transaction log files are copied from backup repository to the Windows machine hosting the target server, so the account used to run Veeam Explorer for Microsoft SQL Server will require appropriate permissions (see Required Permissions for details). Then target server performs log replay with the closest earlier restore point to bring the database to the desired state.
- Staging SQL Server is used in Restore to the state before selected transaction scenario – it presents transaction records to user who selects the undesired transaction and instructs Veeam to restore database to the state prior to that operation. Staging SQL Server is specified on the SQL Server Settings tab of the Options dialog (open from the main menu). By default, local Microsoft SQL Server deployed together with the Veeam backup server is used as a staging system.
Export scenarios are implemented as follows:
- In the Export to current restore point (the one currently mounted to Veeam backup server) scenario, database will be exported as .MDF to the specified target SQL Server, schema objects will be exported with .SQL script file; no staging server is needed.
- For the Export to selected point in time scenario, you will need a staging SQL Server – it will be used for log replay with the closest earlier restore point to bring the database to the desired state. Database file (.mdf) or script file for schema objects (.sql) will be copied to the specified location.
- The Export to the state before selected transaction scenario also requires a staging SQL Server – to present the list of transactions to user and to replay the logs in order to bring the database to the desired state.
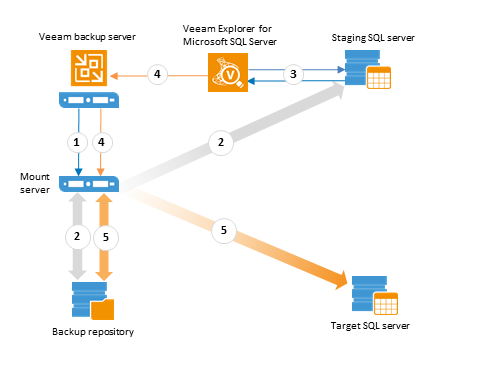
Scenarios involving a staging SQL Server are described below:
- Database files from the SQL Server's backup are mounted to SQL server (staging or target, depending on the required restore scenario).
- In particular, staging server is used in Restore to the state before selected transaction scenario - it presents transaction records to users who select the undesired transaction and instruct Veeam to restore database to the state prior to that operation.
- Veeam Explorer for Microsoft SQL Server obtains SQL server hierarchy information (instances and databases) and presents it to the user.
- A user chooses the database to restore and specifies target location (original or another server), settings required to access that server, as well as the required point in time or undesired transaction.
- Database files (including log files, if necessary) are then copied from the repository to the Windows machine hosting the target server, the database is attached to target SQL server, put in the desired state (using log replay, if necessary) and becomes ready for use.
|
See System Requirements for more information on the staging SQL Server. |
Veeam Explorer needs a staging Microsoft SQL Server for several export scenarios: export to selected point in time and export to the state before selected transaction. The staging SQL Server should meet several requirements listed in this document. Refer to the How Veeam Explorer for Microsoft SQL Server Works and the Staging SQL Server sections for details. You can configure a path to the temporary location on the staging SQL Server where the log files will be stored during export scenarios. There can be other scenarios when you need to configure a path to the temporary folder where data should be stored – for example, when restoring a database from the AlwaysOn Availability Group.
To configure a path to the temporary folder, do the following:
- Go to the %programdata%\Veeam\Backup and Replication\SQLExplorer folder on the machine where Veeam Explorer runs, and locate or create a new configuration file named Config.xml in that folder.
- Locate (or add) the TempFolderPath configuration parameter to the file content and use it to specify the location you need (default is C:\tmp):
<Veeam> |
- Save and close the configuration file.







