This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the current version.
This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the current version.Reverse Incremental Backup
The reverse incremental backup method produces a backup chain that consists of the last full backup and a set of reverse incremental backups preceding it.
Veeam Backup & Replication creates a reverse incremental backup chain in the following way:
- During the first run of a backup job, Veeam Backup & Replication creates a full backup file (VBK) in the backup repository.
- During subsequent backup job sessions, Veeam Backup & Replication copies only VM data blocks that have changed since the last performed backup. Veeam Backup & Replication “injects” copied data blocks into the full backup file to rebuild it to the most recent state of the VM. Additionally, Veeam Backup & Replication creates a reverse incremental backup file (VRB) containing data blocks that are replaced when the full backup file is rebuilt, and adds this reverse incremental backup before the full backup in the backup chain.
After adding a new restore point to the backup chain, Veeam Backup & Replication checks the retention policy set for the job. If Veeam Backup & Replication detects an outdated restore point, it removes this point from the backup chain. For more information, see Retention for Reverse Incremental Backup.
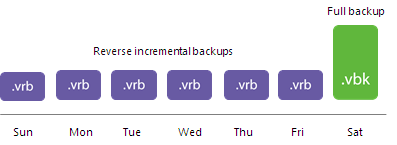
As a result, the most recent restore point in the backup chain is always a full backup, and it gets updated after every successful backup job session.
The reverse incremental backup method enables you to immediately restore a VM to the most recent state without extra processing because the most recent restore point is a full backup file. If you need to restore a VM to a particular point in time, Veeam Backup & Replication applies the required VRB files to the VBK file to get to the required restore point.
To use the reverse incremental backup method, you must select the Reverse incremental option in the backup job settings.