 This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the current version.
This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the current version.Switching Between Synthetic and Active Full Modes
In some cases, you may want to change the algorithm of archive full backup creation. You can:
Switching from Synthetic to Active Full Method
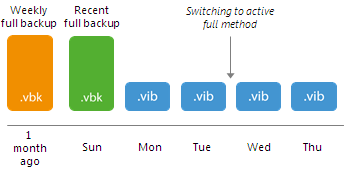
After you switch from the synthetic to the active method of archive backup creation, Veeam Backup & Replication does not perform synthetic transform operations for some time. Veeam Backup & Replication works in the following way:
- Veeam Backup & Replication adds new incremental restore points to the backup chain and keeps existing restore points until a new active full backup is created.
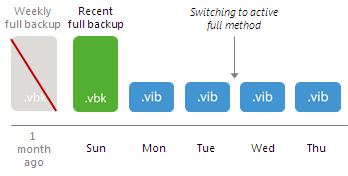
- After the new active full backup is created, Veeam Backup & Replication checks the retention policy set for the job. If some archive full backups are outdated, Veeam Backup & Replication removes them from the backup chain.
- Veeam Backup & Replication keeps adding new incremental restore points to the backup chain. When the number of restore points in the new backup chain is equal to the number allowed by retention, Veeam Backup & Replication removes incremental restore points that precede the new active full backup.
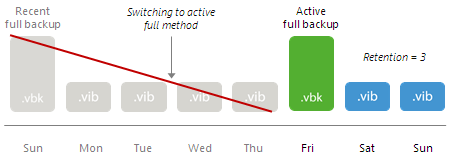
After this, Veeam Backup & Replication uses the new method to create the backup chain in a regular manner.
Switching from Active Full to Synthetic Method
Scenario 1. The backup chain starts with the recent full backup file and contains archive full backups.
After you switch from the active full to the synthetic algorithm of archive backup creation, Veeam Backup & Replication works in the following way:
- During the first synchronization interval after the switch, Veeam Backup & Replication adds a new incremental restore point to the backup chain.
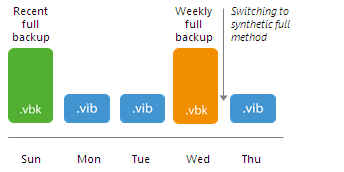
- During the second synchronization interval, Veeam Backup & Replication adds the second incremental restore point to the backup chain and builds a recent full backup out of the latest archive full and first incremental restore point in the backup chain.
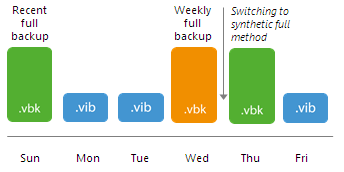
- After that Veeam Backup & Replication uses the new algorithm to create the backup chain in a regular manner.
During every new synchronization interval, Veeam Backup & Replication checks retention settings for the job. Depending on the case, Veeam Backup & Replication deletes outdated restore points in the following manner:
- Case 1. The existing backup chain (backup chain created before the switch) does not contain archive full backups created by the GFS schedule.
When the number of restore points in the new backup chain is equal to the number allowed by the retention policy, Veeam Backup & Replication removes restore points from the backup chain created before the switch.
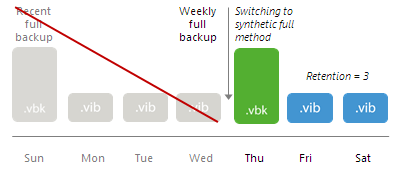
- Case 2. The existing backup chain (backup chain created before the switch) contains archive full backups created by the GFS schedule.
When the number of restore points in the new backup chain is equal to the number allowed by the retention policy, Veeam Backup & Replication starts merging restore points in the existing backup chain until it reaches to the archive full backup. The archive full backup is then set aside as a GFS restore point, and Veeam Backup & Replication keeps working according to the Case 1.
For example, you instruct the backup copy job to create weekly full backups on Tuesday in the active full backup method. Then you switch to the synthetic full backup method. After the switch, Veeam Backup & Replication creates a new recent full backup and adds incremental backups to it. When the number of restore points in the new backup chain is equal to the number allowed by the retention policy, Veeam Backup & Replication starts merging the recent full backup in the existing backup chain created before the switch. When Veeam Backup & Replication reaches the weekly backup created on Tuesday, it sets this weekly backup aside and retains it in the backup repository. After that, Veeam Backup & Replication removes restore points from the existing backup chain.
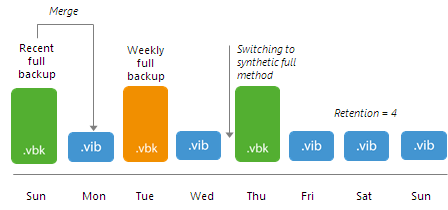
Scenario 2. The backup chain starts with the archive full backup.
After you switch from the active full to the synthetic method of archive backup creation, Veeam Backup & Replication works in the following way:
- During the first synchronization interval after the switch, Veeam Backup & Replication adds a new incremental restore point to the backup chain.
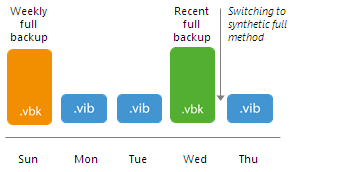
- During the second synchronization interval, Veeam Backup & Replication adds a second incremental restore point to the backup chain and builds the recent full backup out of the latest archive full and the first incremental restore point in the backup chain.
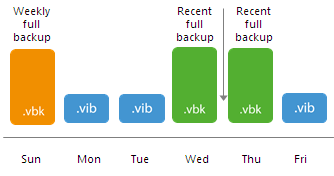
- After that Veeam Backup & Replication uses the new algorithm to create the backup chain in a regular manner. During every new synchronization interval, Veeam Backup & Replication checks retention settings for the job and, if incremental restore points between the archive full backup and recent full backups are outdated, they are removed from the backup chain.
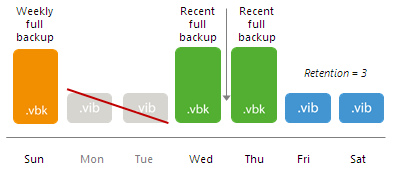
Scenario 3. The backup chain does not contain archive full backup files.
In this case, Veeam Backup & Replication works by the standard archive full backup scheme. For more information, see GFS Retention Policy.