
This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the
current version.
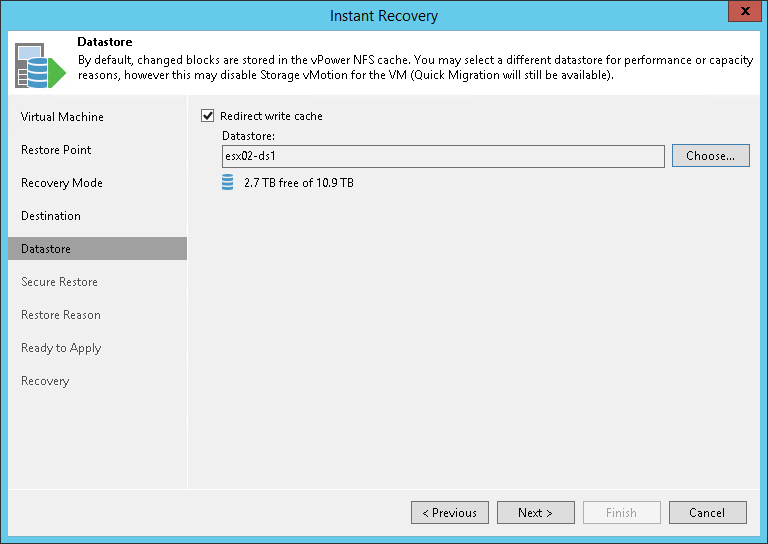
Step 6. Select Destination for Virtual Disk Updates
At the Datastore step of the wizard, you can select where redo logs must be stored when the VM is running from the backup. Redo logs are auxiliary files used to keep changes that take place when VMs run in the virtual lab. By default, redo logs are stored on the vPower NFS server. However, you can store redo logs on any datastore in the virtual environment. Redirecting redo logs improves recovery performance but makes Storage vMotion not possible for ESXi 5.x and earlier. As soon as a recovery verification job completes, Veeam Backup & Replication deletes redo logs.
To redirect redo logs:
- Select the Redirect write cache check box.
- Click Choose and select a datastore from the list.
 Important! Important!
|
Consider the following: - If you migrate the recovered VM to the same datastore cluster that is used as the destination for redirecting virtual disk updates, you must enable the Force Veeam transport usage check box at the Transfer step of the Quick Migration wizard. Otherwise, your migrated workload may be deleted.
- If you migrate the recovered VM to the same datastore which is used as the destination for redirecting virtual disk updates, Veeam Backup & Replication will automatically switch to Veeam Quick Migration instead of using Storage vMotion. The described behavior is implemented to prevent data loss due to a bug in VMware Storage vMotion. Note that using Veeam Quick Migration will cause minimal VM downtime.
- If disks of a restored VM are greater than 2 TB, you must not place redo logs on a VSAN datastore. Otherwise, Veeam Backup & Replication will fail to create a snapshot for the restored VM. For more information, see VMware Docs.
|
 This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the current version.
This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the current version.