 This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the current version.
This is an archive version of the document. To get the most up-to-date information, see the current version.VMware CDP Proxy
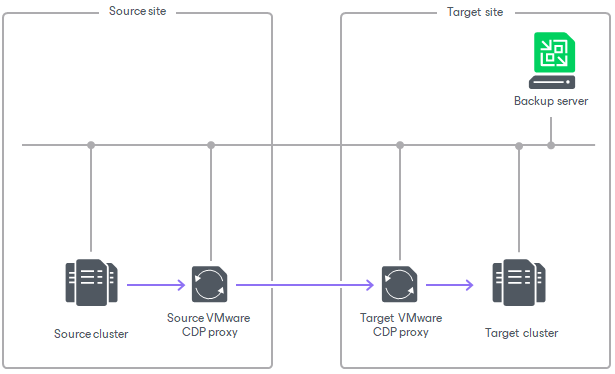
A VMware CDP proxy is a component that operates as a data mover and transfers data between the source and target hosts. Basically, VMware CDP proxy performs the following tasks:
- Receives VM data from the production storage
- Aggregates changed data
- Prepares data for short-term restore points
- Compresses and deduplicates data
- Encrypts and decrypts data
- Sends data to the storage in the disaster recovery site or another VMware CDP proxy
VMware CDP Proxy Deployment
You can assign the role of a VMware CDP proxy to any Windows-managed virtual or physical server added to your Veeam Backup & Replication infrastructure. For information on how to add a server, see Adding Microsoft Windows Servers. For information on how to assign the VMware CDP proxy role, see Adding VMware CDP Proxies.
We recommend you to configure at least two VMware CDP proxies: one (source proxy) in the production site and one (target proxy) in the disaster recovery site. To optimize performance of several concurrent tasks, you can use several VMware CDP proxies in each site. In this case, Veeam Backup & Replication will distribute the restore workload between available proxies on per-task basis, taking into account proxy connectivity and their current load. For more information on which proxies are considered the most appropriate for continuous data protection, see How CDP Works.
Design your system in such a way that one VMware CDP proxy is used only as a source or only as target proxy.
For example, if you have cross cluster or cross host replication (from ESXi 1 to ESXi 2, and from ESXi 2 to ESXi 1), it is better to have four VMware CDP proxies: one source proxy and one target proxy for data flow from ESXi 1 to ESXi 2, and one source proxy and one target proxy for data flow from ESXi 2 to ESXi 1.
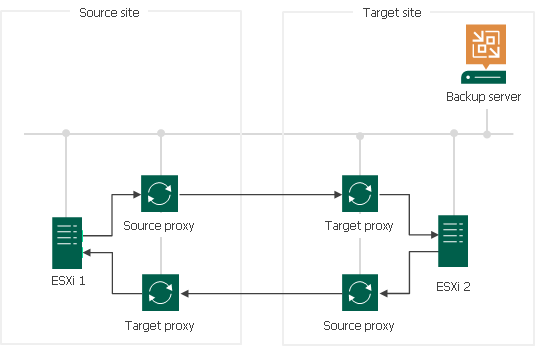
Note |
If you deploy VMware CDP proxies on virtual machines, we recommend you to locate source proxies on the source host, target proxies on the target host. |
VMware CDP Proxy Services and Components
VMware CDP proxies run light-weight services that take a few seconds to deploy. Deployment is fully automated. Veeam Backup & Replication installs the following components and services:
- Veeam CDP Proxy Service manages all CDP activities such as data aggregation, data compression and decompression, data transfer and other.
- Veeam Installer Service is an auxiliary service that is installed and started on any Windows server once it is added to the list of managed servers in the Veeam Backup & Replication console. This service analyzes the system, installs and upgrades necessary components and services depending on the role selected for the server.
- Veeam Data Mover handles traffic sent during failback.
By default, VMware CDP proxies store the received data into RAM. If a VMware CDP proxy gets overloaded and the memory runs out, the proxy starts storing data into the cache. Data is deleted from the cache or memory only after the proxy gets a notification that the target host has successfully saved data sent by the proxy.
If the cache gets full and there is no "free" VMware CDP proxy, Veeam Backup & Replication will stop the CDP process. CDP will be resumed only after a new or "free" proxy appears, or after the proxy cache gets free space.
From the technical point of view, the cache is a folder on a VMware CDP proxy. We recommend you to allocate at least 10 GB or 1 GB per each VM disk if you plan to protect more than 10 disks in one CDP policy. Also, the longer RPO you set in a CDP policy, the larger cache you may need.
Requirements for VMware CDP Proxy
Before you assign the role of a backup proxy, check the following requirements:
- For system requirements, see System Requirements for VMware CDP Proxy Server.
- A VMware CDP proxy must be a Windows-managed virtual or physical server.
- [For VMware CDP proxies deployed on physical servers] Fast network between hosts and VMware CDP proxies is required.