Changed Block Tracking
To perform incremental backup, Veeam Backup & Replication needs to know what data blocks have changed since the previous job session.
For VMware VMs with hardware version 7 and later, Veeam Backup & Replication employs a native VMware vSphere feature — VMware vSphere Changed Block Tracking (CBT). Instead of scanning VMware VMFS (Virtual Machine File System), Veeam Backup & Replication queries CBT through VMware VADP (VMware vStorage API for Data Protection) and gets a list of blocks that have changed since the last job session. The use of CBT increases the speed and efficiency of block‑level incremental backups.

Veeam Backup & Replication uses CBT for the following operations:
- Backup
- Replication
- Entire VM restore
- VM disk restore
Veeam Backup & Replication enables CBT by default. If necessary, you can disable it in job settings.
NotE |
Mind the following:
|
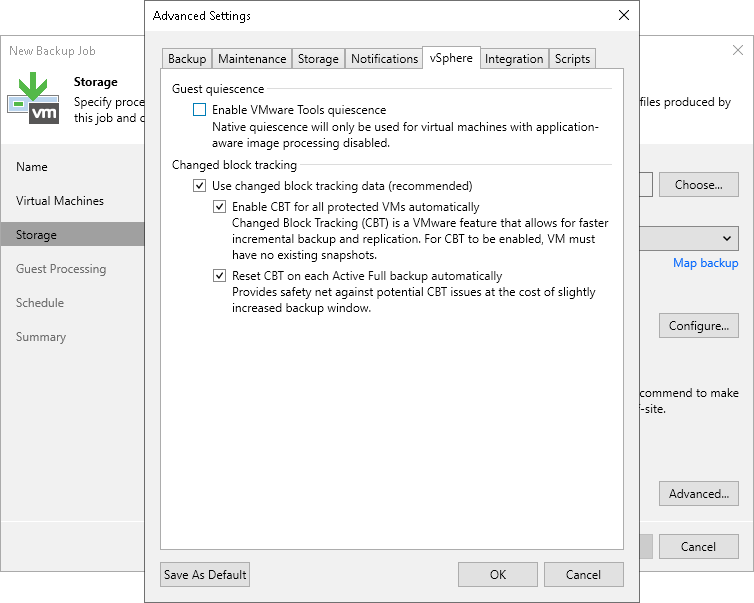
Note |
For VMs with virtual disks in thin format, Veeam Backup & Replication also uses CBT during active full backup sessions to detect unallocated regions of virtual disks and skip them. For VMs with virtual disks on an NFS datastore, Veeam Backup & Replication uses CBT as well but cannot leverage CBT on the first full run. |
In some situations, Veeam Backup & Replication cannot leverage VMware vSphere CBT, for example, if VMs run an earlier version of virtual hardware. If Veeam Backup & Replication cannot leverage VMware vSphere CBT, it fails over to the Veeam proprietary filtering mechanism. Instead of tracking changed blocks of data, Veeam Backup & Replication filters out unchanged data blocks.
During VM processing, Veeam Backup & Replication consolidates virtual disk content, scans through the VM image and calculates a checksum for every data block. Checksums are stored as metadata to backup files next to VM data. When incremental backup is run, Veeam Backup & Replication opens all backup files in the chain of previous full and incremental backups, reads metadata from these files and compares it with checksums calculated for a VM in its current state. If a match is found (which means the block already exists in the backup), this block is filtered out.