Step 9. Configure Seeding and Mapping
The Seeding step is available if you have selected the Replica seeding check box at the Name step of the wizard.
At the Seeding step of the wizard, configure replica seeding and mapping. Seeding and mapping help reduce the amount of traffic sent during the initial replica synchronization. For more information on when to use seeding and mapping, see Replica Seeding and Mapping.
Important |
If the Replica seeding check box is enabled in a policy, all VMs in the policy must be covered with seeding or mapping. If a VM is neither has a seed, nor is mapped to an existing VM, it will be skipped from processing. |
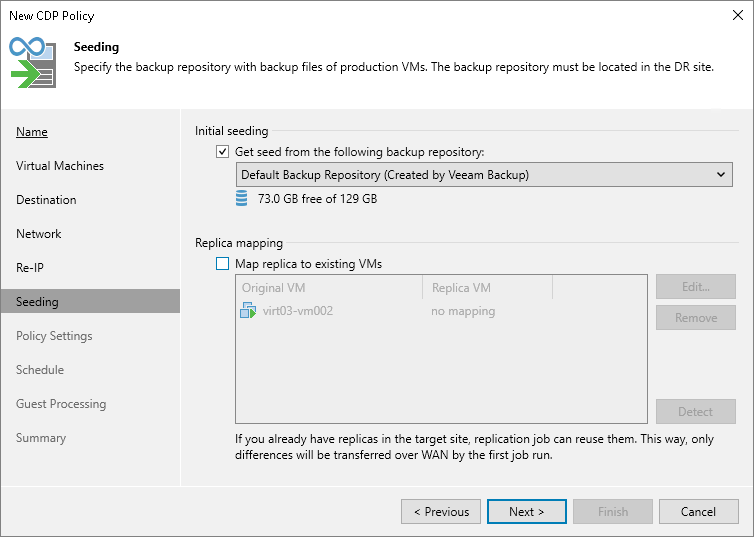
To configure replica seeding:
- Make sure that you have backups of replicated VMs in a backup repository in the DR site. If you do not have the backups, create them as described in section Creating Replica Seeds for CDP.
Important |
Consider the following:
|
- Select the Get seed from the following backup repository check box.
- From the list of available backup repositories, select the repository where your replica seeds are stored.
Note |
If a VM has a seed and is mapped to an existing replica, replication will be performed using replica mapping because mapping has a higher priority. |
To configure replica mapping:
- Select the Map replicas to existing VMs check box.
- If you want Veeam Backup & Replication to scan the DR site to detect existing copies of VMs that you plan to replicate, click Detect.
If any matches are found, Veeam Backup & Replication will populate the mapping table. If Veeam Backup & Replication does not find a match, you can map a VM to its copy manually.
- If you want to map a VM manually, select a source VM from the list, click Edit and select the copy of this VM on the target host in the DR site.
To remove a mapping association, select a VM in the list and click Remove.