Step 3. Select Failback Destination
At the Destination step of the wizard, select a failback destination and backup proxies for data transfer during failback:
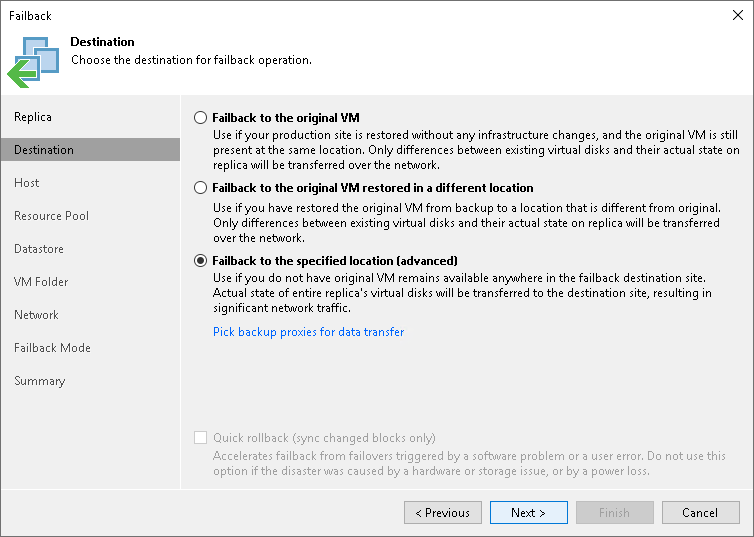
- Select a destination for failback. Veeam Backup & Replication supports the following options:
- Failback to the original VM — select this option if you want to fail back to the source VMs that reside on the source hosts. Veeam Backup & Replication will synchronize the state of the source VMs with the current state of their replicas to apply any changes that occurred to the replicas while running in the DR site.
If you select this option, you will proceed to the Failback Mode step of the wizard.
- Failback to the original VM restored in a different location — select this option if the source VMs have already been recovered to a new location, and you want to switch to the recovered VMs from their replicas. Veeam Backup & Replication will synchronize the state of the recovered VMs with the current state of the replicas to apply any changes that occurred to the replicas while running in the DR site.
If you select this option, you will proceed to the Target VM step of the wizard.
- Failback to the specified location — select this option if you want to recover VMs from replicas. You can recover VMs to a new location, or to any location but with different settings (such as network settings, virtual disk type, configuration file path and so on). Select this option if there is no way to fail back to the source VM or an already recovered VM.
If you select this option, the wizard will include additional steps.
If you select one of the first two options, Veeam Backup & Replication will send to the source/recovered VMs only differences between the existing virtual disks. Veeam Backup & Replication will not send replica configuration changes such as different IP address or network settings (if replica Re-IP and network mapping were applied), new hardware or virtual disks added while the replicas were in the Failover state.
If you select Failback to the specified location, Veeam Backup & Replication will send to the specified location whole VM data, including VM configurations and virtual disk content.
- To select which backup proxies will be used for data transfer, click Pick backup proxies for data transfer. By default, Veeam Backup & Replication selects proxies automatically.
If you leave automatic proxy selection, Veeam Backup & Replication will check available backup proxies before processing each VM from the VM list. If more than one backup proxy is available, Veeam Backup & Replication analyzes transport modes that the backup proxies can use, the current workload on the backup proxies to select the most appropriate resource for VM processing.
If you want to assign proxies manually, use the following instructions. If VMs and their replicas reside in different sites, select at least one backup proxy in the production site and one proxy in the disaster recovery site. If VMs and replicas reside in the same site, you can use the same backup proxy as the source and target one. We recommend you to select at least two backup proxies in each site to ensure that failback will be performed in case one proxy fails or looses the network connection.
- [For VMware vSphere prior to version 7.0; for failback to the original VMs] If you want to fasten failback, and the source VMs had problems at the guest OS level, select the Quick rollback check box. For more information on quick rollback, its requirements and limitations, see Quick Rollback.
Restoring Storage Policies
If the replicated VM was associated with the storage policy, in the failback to source location scenario, Veeam Backup & Replication will associate the restored VM with this storage policy.
When you click Next, Veeam Backup & Replication will check storage policies in the virtual environment and compare this information with the information about the replica storage policy. If the original storage policy has been changed or deleted, Veeam Backup & Replication will display a warning. You can select one of the following options:
- Current — the restored VM will be associated with the profile with which the source VM in the production environment is currently associated.
- Default — the restored VM will be associated with the profile that is set as default for the target datastore.
- Stored — the restored VM will be associated with the profile that was assigned to the source VM at the moment of replication.
For more information, see Storage Profiles.